So far, you’ve learned how to create an S3 bucket and upload files to it. But did you know you can use Amazon S3 to host an entire website? For simple sites that don’t require a backend server—known as “static websites”—S3 provides an incredibly cheap, reliable, and massively scalable hosting solution.
A static website is one built using only HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. It’s perfect for portfolios, landing pages, documentation sites, or simple blogs. In this tutorial, we will walk you through the entire process of hosting your first static website on S3, making it publicly accessible on the internet.
Prerequisites
- An active AWS Account.
- An S3 bucket already created. If you haven’t done this, follow our guide on how to create an S3 bucket.
Step 1: Create a Simple Website File
First, we need a website to host. We’ll create a very simple HTML file.
- Open a plain text editor on your computer (like Notepad on Windows or TextEdit on Mac).
- Copy and paste the following HTML code into the editor:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>My Awesome Website</title>
</head>
<body style="font-family: sans-serif; text-align: center; margin-top: 50px;">
<h1>Welcome to My Website!</h1>
<p>This site is hosted on Amazon S3.</p>
</body>
</html>
- Save this file with the exact name
index.html. This is the default file that web browsers look for when visiting a website.
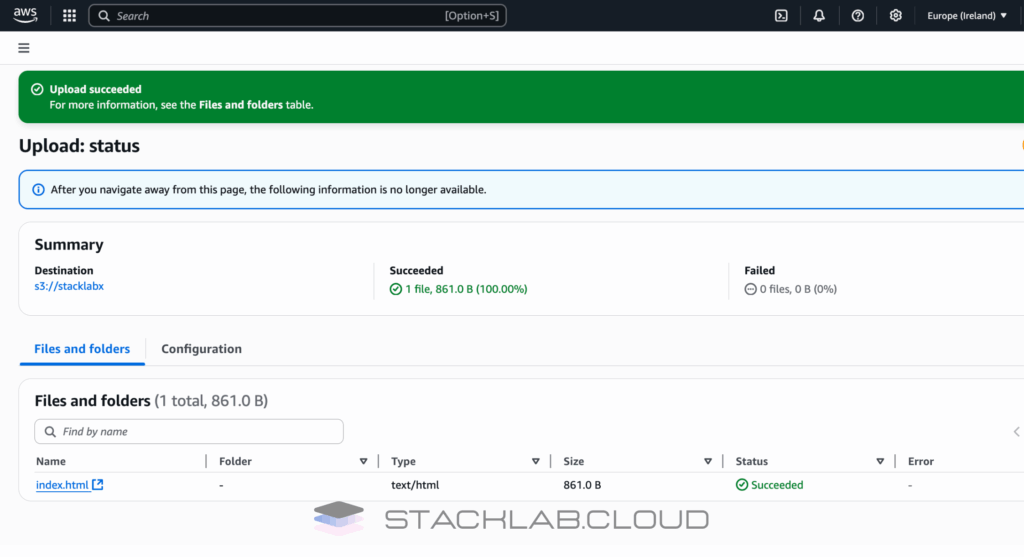
Step 2: Upload Your Website File to S3
Now, let’s upload our new `index.html` file to the S3 bucket you created earlier.
- Navigate to the S3 Console in AWS.
- Click on the name of your bucket.
- Click the “Upload” button.
- Click “Add files” and select the `index.html` file you just saved.
- Click the “Upload” button at the bottom of the page to complete the upload.
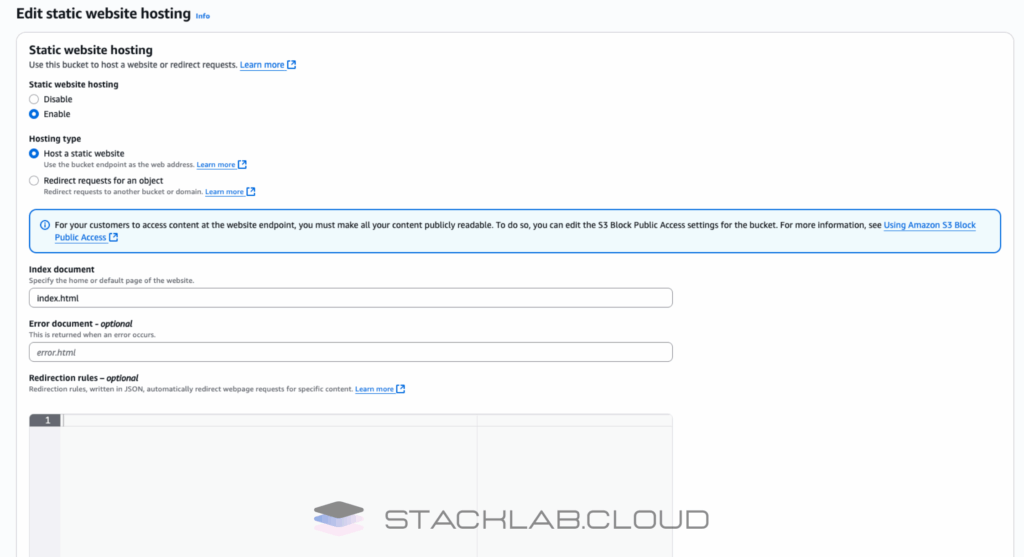
Step 3: Enable Static Website Hosting
By default, an S3 bucket is just a private container for files. We need to tell AWS to treat it like a web server.
- Inside your S3 bucket, click on the “Properties” tab.
- Scroll all the way down to the bottom to find the section called “Static website hosting”.
- Click the “Edit” button.
- Select the option to “Enable” static website hosting.
- In the “Index document” field, type
index.html. - Leave the “Error document” field blank for now.
- Click “Save changes”.
After saving, scroll back down to the “Static website hosting” section. You will now see a unique Bucket website endpoint URL. This is the public URL for your new website. Don’t click it yet—it won’t work until we complete the next step.
Step 4: Make Your Bucket Contents Public
Even though we’ve enabled web hosting, the files inside the bucket are still private. We need to create a “Bucket Policy” to grant the public read-only access to the objects in our bucket.
- Inside your S3 bucket, click on the “Permissions” tab.
- Under “Block public access,” click “Edit”. Uncheck the box for “Block all public access” and click “Save changes”. You will need to type `confirm` to apply this change.
- Now, scroll down to the “Bucket policy” section and click “Edit”.
- Copy the following JSON policy and paste it into the policy editor.
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "Statement1",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": "*",
"Action": "s3:GetObject",
"Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::YOUR_BUCKET_NAME/*"
}
]
}
- CRITICAL: You must replace
YOUR_BUCKET_NAMEin the policy with the actual name of your bucket. - Click “Save changes”.
Step 5: Test Your Website!
You’re all set. It’s time to see your live website.
- Go back to the “Properties” tab of your bucket.
- Scroll down to the “Static website hosting” section.
- Click on the Bucket website endpoint URL.
A new browser tab should open, and you will see your “Welcome to My Website!” message. Congratulations, your website is now live on the internet, hosted entirely on Amazon S3!

Conclusion
Hosting a static website on S3 is a powerful, low-cost solution for many projects. You’ve now learned how to configure a bucket for web hosting and how to set the necessary permissions to make your content public. This is a fantastic project to add to your cloud portfolio and a key skill for any AWS user.
Read Next: How to Use a Custom Domain for Your S3 Website with Route 53
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a static website?
A static website is a type of website that is delivered to a user’s web browser exactly as it is stored. It consists of fixed content, and each page is coded in HTML and displays the same information to every visitor. Unlike dynamic websites, they do not require any server-side processing or databases. This makes them simpler, faster, and cheaper to host.
Why use AWS S3 for hosting?
AWS S3 (Simple Storage Service) is an excellent choice for hosting static websites for several reasons:
Cost-effective: S3 is very affordable, especially for low-traffic sites.
Scalability: It can handle large amounts of traffic and data, scaling automatically as your needs grow.
High availability and durability: S3 is designed for 99.999999999% durability and 99.99% availability of objects over a given year.
Easy to use: Setting up a static website on S3 is a straightforward process that can be done in a few steps.
What are the main steps to host a static website on S3?
The process of hosting a static website on S3 generally involves these steps:
Create an S3 bucket: This is where you will store your website files.
Enable static website hosting: You need to configure the bucket to serve website content.
Upload your website files: This includes your HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and any other assets.
Set public access permissions: You need to make your files publicly readable so that visitors can access them.
Test your website: You can then access your website using the endpoint provided by S3.
Do I need a domain name?
While you can access your website using the S3 endpoint, it’s recommended to use a custom domain name for a more professional look. You can register a domain name with Amazon Route 53 or any other domain registrar.
How do I update my website?
To update your website, you simply need to upload the new or modified files to your S3 bucket. The changes will be reflected on your website almost immediately.
What about security?
You can use AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) to control access to your S3 bucket. Additionally, you can use a bucket policy to grant public read access to your website while keeping other permissions restricted.











